CIS and CIS E are two types of systems mostly used in VW engines. We see a lot of people are interested in knowing more about these two systems because of the differences between them.
In this article, we discuss almost everything you need to know about CIS and CIS E systems in broad and simple terms. So stick around until the end.
What is CIS in cars?
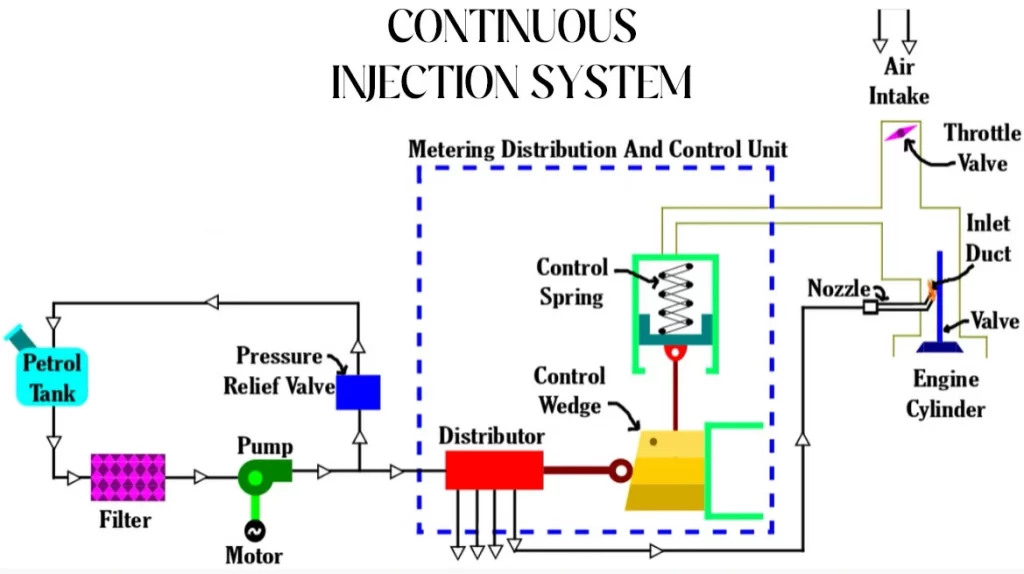
CIS, or Continuous Injection System, is a gasoline injection mechanism that is considerably different from that used in modern automobiles.
Fuel is sprayed constantly, rather than in short bursts at regular intervals as in contemporary cars.
The volume of fuel is controlled by the air intake stream. The coolant temperature determines when to apply oxygen sensor regulation, and the oxygen sensor regulation further controls the volume of fuel.
It’s a tight system of checks and balances that can self-correct using only a few electronic components.
What is fuel injection in cars?
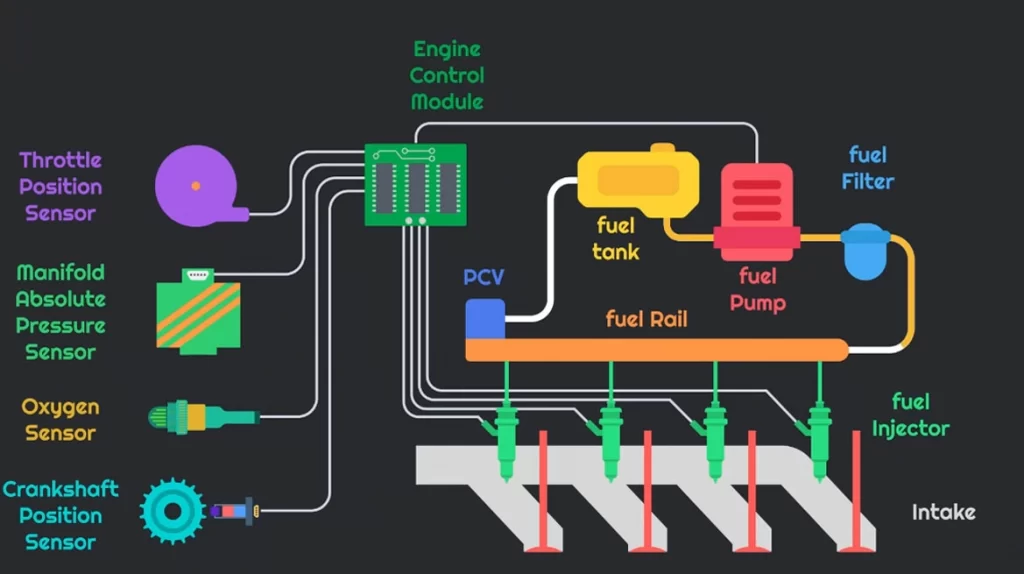
All fuel injection systems have three basic components: at least one fuel injector (also known as an injection valve), a mechanism that generates enough injection pressure, and a device that measures the correct amount of fuel.
These three basic components might be independent devices (one or more fuel injectors, a fuel distributor, and a fuel pump), an injection valve and an injection pump, or totally integrated devices (an injection valve and an injection pump) (a unit injector).
What is a CIS system?
A single wire oxygen sensor and a cast iron (typically black or rusted) gasoline distributor are used in the CIS system.
A three-wire oxygen sensor and an aluminum fuel distributor with a grey plastic “box” on the side are used in the CIS E system. The differential pressure regulator is seen here (DPR).
There is no knock box, no O2 sensor, and no ECU in a basic CIS. It’s extremely basic, but when properly configured, it performs wonderfully.
The fuel distributor in all CIS systems receives fuel from the fuel pump. The fuel is then redirected (distributed) into two locations. One leads to the lower chamber, while the other leads to the upper chamber.
The lower chamber is the “supply” chamber, which feeds the plunger hole and the injectors. The mixture control chamber is located in the upper chamber.
What is CIS E?
These are continuous systems, like CIS, in that the injectors deliver fuel continuously rather than opening and closing to manage fuel delivery.
The fuel injectors’ primary duty is to atomize the flow of fuel provided under pressure from the fuel distributor.
The CIS E system varies from the previous CIS system in that it has more electronic controls to more precisely regulate fuel pressures and control fuel mixing.
The CIS E Motronic engine management system integrates electronic control of CIS E fuel injection, evaporative emissions, ignition, and idle speed.
How does Bosch CIS work?
The Bosch CIS s a hydraulic-type fuel injection system that controls injection quantity via an airflow sensor mechanically coupled to a hydraulic valve. The Lambda system is a feedback control capable of sensing and constantly modifying air/fuel ratios.
What 3 types of injection systems exist?
There are mainly three kinds of injection systems used in vehicle engines, they are multipoint injection, indirect injection, and direct injection.
Multi-point injection.
Rather than injecting fuel at a central point within an intake manifold, multi-point injection injects fuel into the intake ports just upstream of each cylinder’s intake valve.
Multi-point injected systems typically employ numerous fuel injectors. However, other systems, such as GM’s central port injection system, employ tubes with poppet valves supplied by a central injector rather than multiple injectors.
What is an MPI engine?
MPI, or Multi-Point Injection, is one of the most used systems today, with gasoline pumped into each intake port. However, even in MPI engines, fuel supply responsiveness and combustion control are limited since gasoline mixes with air before entering the cylinder.
Direct injection.
An engine with direct injection has a single combustion chamber, and the gasoline is fed directly into it.
This can be accomplished with either an air blast (air-blast injection) or hydraulically. In-car engines, the latter method is significantly more popular.
Hydraulic direct injection systems typically spray fuel into the air within the cylinder or combustion chamber, although some systems spray fuel against the combustion chamber walls.
Indirect injection.
There are two combustion chambers in an indirect-injected engine: a primary combustion chamber and a pre-chamber (also known as an ante-chamber) that is connected to the main one.
The fuel is only fed into the pre-chamber (where it begins to burn) rather than the main combustion chamber. As a result, this principle is known as “indirect injection.”
Which injection system is used in a diesel engine?
You may already be aware that a diesel engine is a self-igniting engine. This signifies that the combustion will happen on its own. Various factors can trigger self-ignition.
Because fuel atomizes in a high-pressure chamber, this is the most dominant. The air pressure in the chamber is greater than the flash point of diesel fuel. When atomized, this is what causes fuel to burn spontaneously.
Some related FAQs about CIS vs. CIS E.
Which is better: MPFI or direct injection?
The fuel is injected after the compression stroke with a direct injection system. It functions at a lower pressure than DI does. It used a higher pressure than MPFI. It is less effective than the DI system.
Which is better, MPI or GDI?
When compared to conventional MPI engines of equivalent size, the GDI engine produces 10% more output and torque at all speeds. The GDI engine provides exceptional acceleration in high-output mode.
Is GDI a turbo?
The letters GDI and T stand for Gasoline Direct Injection and Turbo, respectively. This involves a shift away from multi-point injection (MPI), in which injectors shoot fuel into the inlet tract, and toward the more efficient GDI, in which injectors fire directly into the combustion chamber.
What is the difference between FI and a carburetor?
A fuel injection system precisely provides the proper amount of fuel and may be tweaked based on numerous characteristics, resulting in less fuel waste and improved fuel efficiency. A carburetor cannot alter the fuel ratio based on engine circumstances.
We hope that our explanation provided you with the answer to your question, “CIS vs. CIS E” If you have any additional questions, please leave a comment below, and we will be happy to assist you further. Check out this link for an answers for Ford Taurus Misfire. Thank you very much.
